Due Diligence: ABRAMS world trade wiki for Due Diligence
Dr. Jürgen Abrams, inigma LLC. ABRAMS world trade wiki is a division of inigma LLC
Due diligence is a vital component of the M&A process and involves a detailed review of the target. This includes analyzing financial data such as balance sheets and income statements, legal documentation including contracts and compliance records, operational metrics like supply chain efficiency, and intangible assets such as intellectual property and brand value. The goal is to identify risks and opportunities to make informed decisions. This section explains the basics and the significance of due diligence and where ABRAMS world trade wiki supports this step of an M&A process.
1.1 Why ABRAMS world trade wiki for DD?
The examination centers on a comprehensive analysis that encompasses the financial, operational, and strategic dimensions pertaining to a particular target company, thereby facilitating an in-depth understanding of its overall performance and market positioning.
The breadth of this examination encompasses a comprehensive review of both vendors and clients, a meticulous evaluation of supply chain weaknesses and threats, alongside a detailed investigation into the essential importance of performing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) due diligence within the current corporate environment.
ABRAMS world trade wiki serves as a valuable resource for identifying concealed risks, conducting a meticulous analysis of supply chain intelligence, and effectively benchmarking competitive positions within the broader market framework.
1.2 Operational Due Diligence
This section focuses on evaluating the target’s operational processes, products purchased or sold. Business partners and supply chain details are analyzed. A thorough operational due diligence process includes the following subcategories:
Supplier Due Diligence
Understanding the target’s supplier landscape is crucial to mitigating risks and ensuring operational stability post-acquisition. Key evaluation criteria include:
Supply chain Risk Mitigation: Assess the target's ability to manage risks within its supply chain. This includes analyzing exposure to critical suppliers, identifying alternate sourcing strategies, and evaluating the potential impact of geopolitical risks or natural disasters on supply continuity.
Check Direct Suppliers (Tier 1): Review the target’s relationships with its immediate suppliers by examining existing contracts, delivery performance, and quality standards. This helps to determine supplier reliability and whether current agreements align with the strategic goals of the acquiring company.
Identify Suppliers of Suppliers (Multi-Tier Levels): Investigate the broader supply chain network beyond direct suppliers to identify vulnerabilities in the multi-tier structure. This involves assessing second tier and beyond suppliers for their dependency on critical raw materials or critical suppliers, which could introduce hidden risks to the target’s operations.
Customer Due Diligence
Analyzing the customer base is equally critical to understanding revenue stability and market reach. Key evaluation criteria include:
Supply chain Risk Mitigation: Evaluate the risks related to customer dependencies, such as reliance on a few large customers or the potential for demand fluctuations caused by market or economic changes. This analysis helps identify areas where the customer base may need diversification to reduce risk.
Check Direct Customers: Assess the target’s relationships with its primary customers by analyzing customer satisfaction metrics, revenue concentration, and the stability of existing contracts. Understanding these factors helps determine the sustainability of the target’s revenue streams and potential opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
Identify Customers of Customers (Multi-Tier Level): Investigate the downstream customer ecosystem to understand how the target’s products or services impact end-users. By analyzing the broader demand drivers and potential bottlenecks in the multi-tier customer network, companies can identify risks and opportunities that influence long-term revenue growth and market reach.
Sustainability and ESG Due Diligence
This topic explores the assessment of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors and their growing importance in the M&A process. However, as Sustainability and ESG is currently not the main focus of ABRAMS world trade wiki, it will not be further described here.
1.3 ABRAMS world trade wiki – Insights during the Due Diligence
The platform ABRAMS world trade wiki offers powerful tools and resources to enhance various aspects of the due diligence process. Through its solutions for company transparency, supply chain intelligence, and competitive intelligence, the platform addresses critical challenges in the following ways:
Company Transparency
This solution provides comprehensive profiles of potential targets, including suppliers, customers, purchasing volume, sales volume as well as information on product prices. Access to such detailed information helps uncover hidden risks and ensure a thorough understanding of the target’s operations and governance.
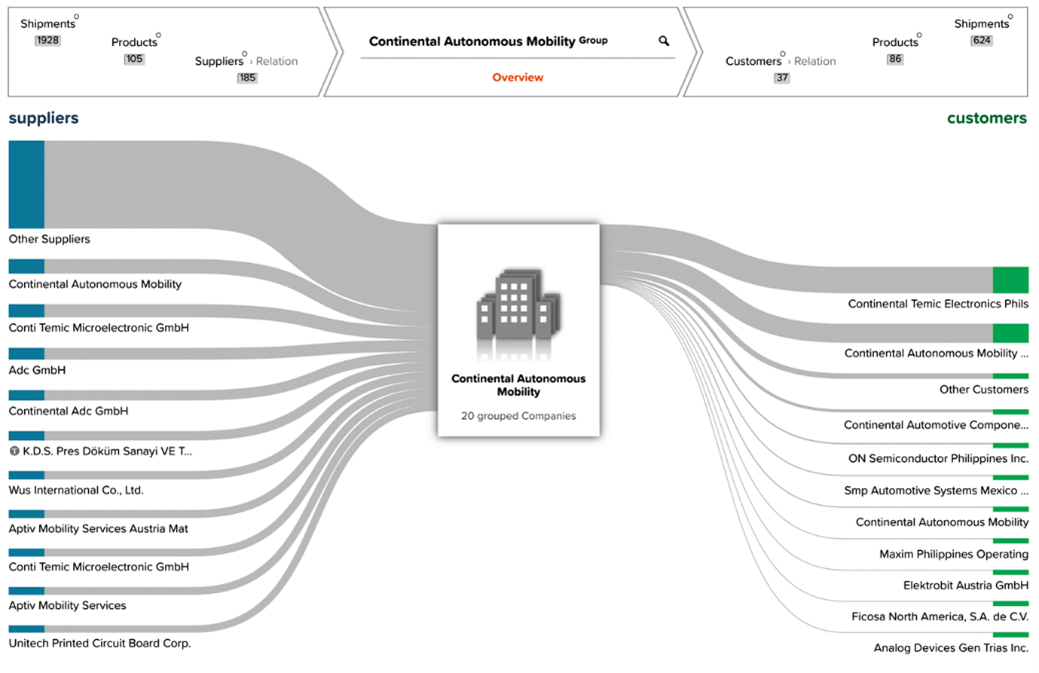
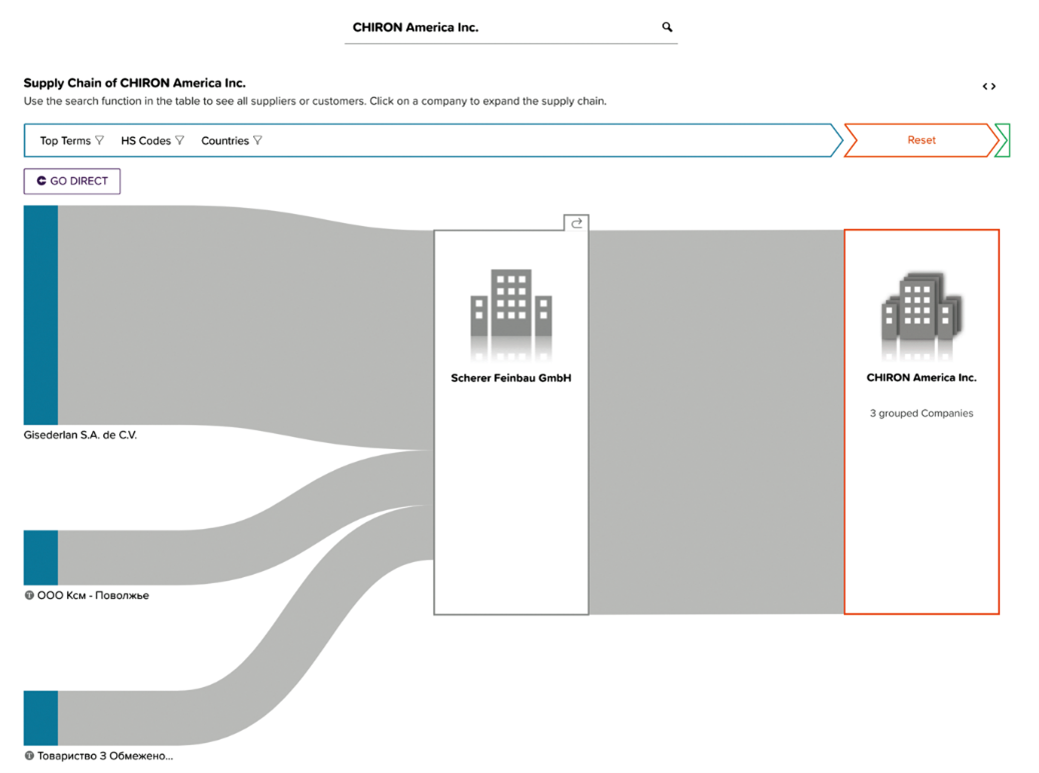
The illustrated example presents a comprehensive Sankey Diagram that meticulously delineates the principal suppliers along with the corresponding customers associated with a hypothetical target company called “Continental Autonomous Mobility”.
Figure 15: Company Transparency: Sankey Diagram with suppliers and customers
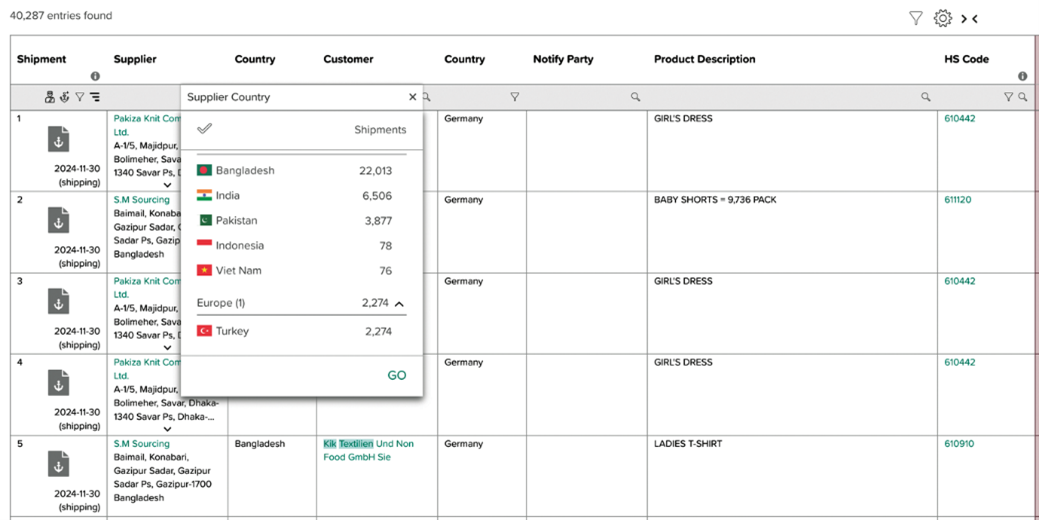
The following example relates to an anonymized apparel importer. The detailed shipment information in the next picture provides an exhaustive overview regarding the predominant nations from which the apparel company imports from with a significant and noteworthy emphasis placed on Bangladesh, which serves as the paramount source of the imported goods that are integral to their operational framework. Further countries are India, Pakistan, Indonesia, and Vietnam.
Figure 16: Company Transparency: Shipment details showing the main sourcing countries
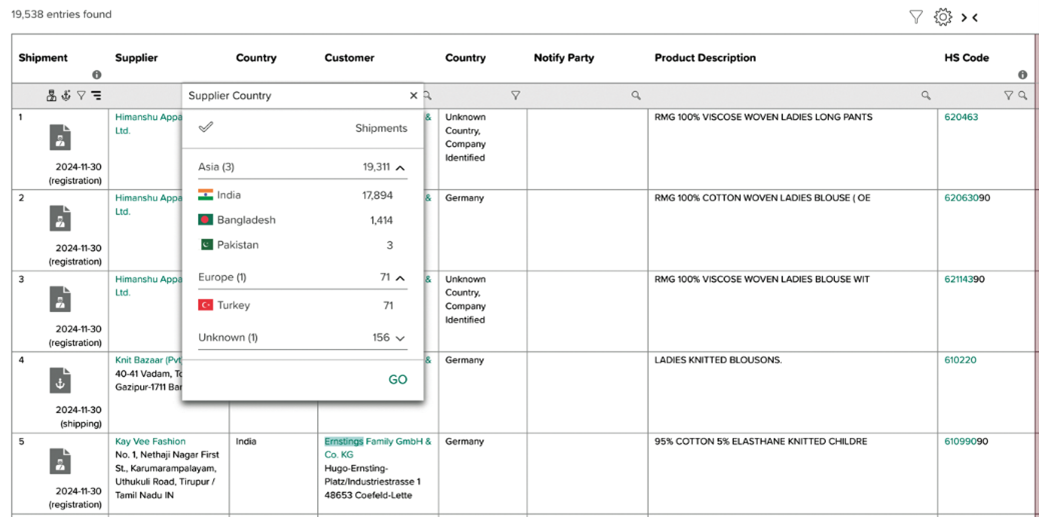
In the subsequent illustration, we will examine yet another anonymized import company specializing in apparel, whose main source for acquiring goods predominantly stems from the diverse and vibrant market of India. In the accompanying image, one can observe a detailed breakdown of the shipment particulars, which furnish an extensive and thorough overview of the key sourcing nations that are intricately linked with that theoretical target enterprise, providing valuable insights into its supply chain dynamics.
Figure 17: Company Transparency: Shipment details of another target showing the main sourcing countries
Supply Chain Intelligence
Supply chain intelligence allows users to analyze the supply chain network of the target, including identifying key suppliers, their locations, and dependencies. This helps in:
Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential supply chain vulnerabilities, such as reliance on a single supplier or exposure to geopolitical risks.
Operational Insights: Gaining clarity on supply chain efficiency and adaptability to disruptions, ensuring the target’s operational stability post-acquisition.
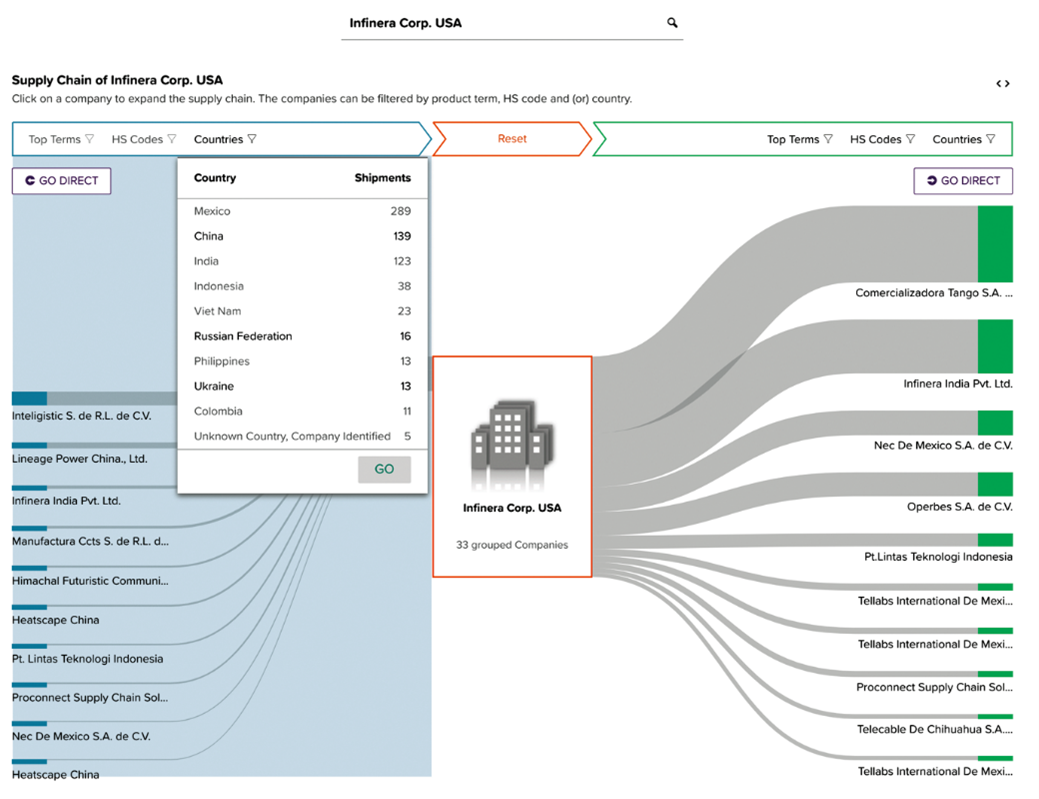
The next screenshot provides a comprehensive overview of the potential vulnerabilities within the supply chain of „Infinera Corp“, which may arise from factors such as an over-dependence on a singular supplier or the heightened exposure to various geopolitical risks that can significantly impact operations.
ABRAMS world trade wiki serves as a robust tool that facilitates the automatic identification of shipments originating from suppliers who may potentially be implicated in geopolitical risks, including but not limited to regions such as China and the Russian Federation, thus enhancing risk management strategies and decision-making processes.
Figure 18: Supply Chain Intelligence: Automatically identifying shipments from suppliers
The following picture provides a comprehensive demonstration of the methods employed to assess possible weaknesses within the supply chain framework, extending our focus well beyond just the immediate tier one suppliers. In the realm of Supply Chain Intelligence, this involves the critical process of pinpointing and analyzing shipments originating from various suppliers that may be at risk due to geopolitical uncertainties, thereby transcending the limitations imposed by merely considering Tier 1 suppliers and embracing a Multi-Tier-Transparency approach.
Figure 19: Supply Chain Intelligence: identifying shipments with geopolitical risks – beyond Tier 1 (Multi-Tier-Transparency)
Competitive Intelligence
This solution enables a deep dive into the target’s competitive landscape, including benchmarking against industry peers. Key benefits include:
Market Position Analysis: Understanding the target’s strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors.
Opportunity Identification: Spotting areas where the target could gain a competitive advantage through synergies with the acquiring company.
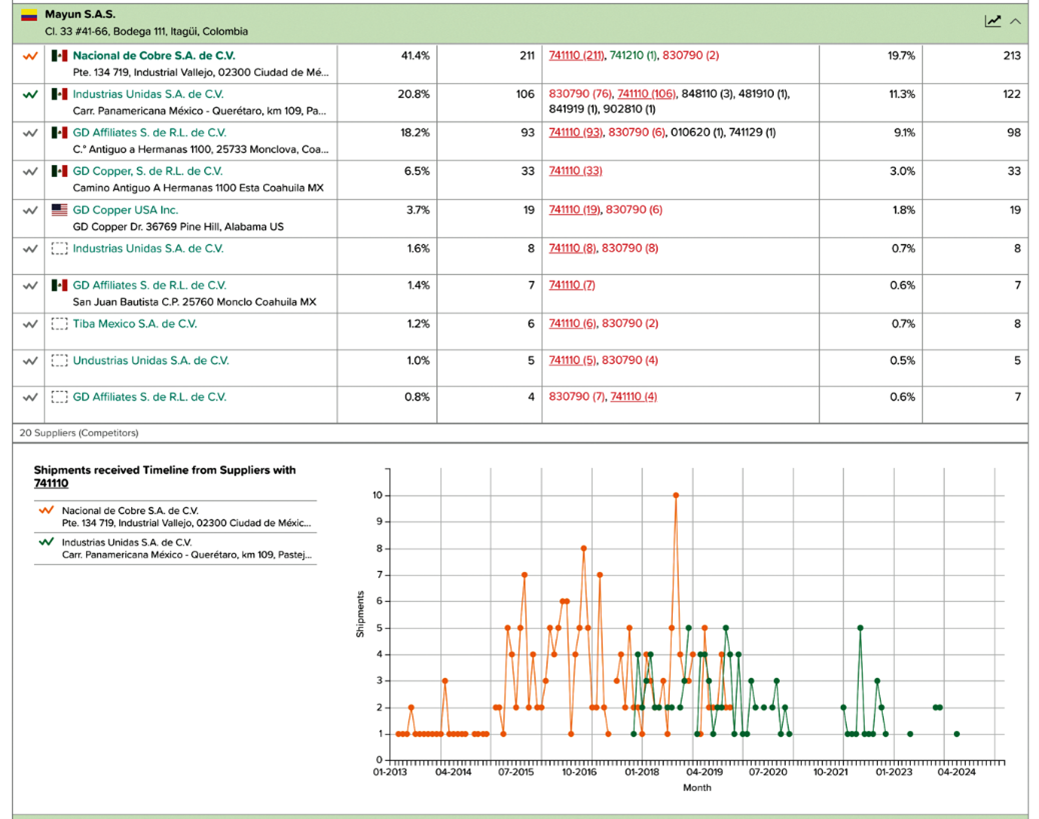
Here is a Competitive Intelligence example relating to a target company that has Mayun SAS in Columbia as a customer. The intricate and comprehensive details regarding shipments provide valuable insights that can significantly illuminate the competitive positioning of a target company, specifically highlighting Mayun as a significant customer while also emphasizing Nacional de Cobre as a major supplier in the past, which may now be considered a potential merger and acquisition target that is presently at risk, especially as it is being substituted or replaced by the emerging player, Industrias Unidas, in this dynamic market landscape.
Figure 20: Competitive Intelligence: Shipment details giving insights into the competitive position
1.4 Conclusion
With ABRAMS world trade wiki, acquirers can conduct a more informed, efficient, and comprehensive due diligence. This enhances the ability to identify risks, validate assumptions, and uncover opportunities that drive successful M&A outcomes.
Abrams brings you value:
Faster, well-founded analyses for pitch and execution
Deeper insights (e.g., supply-chain risks, market modeling) that are often not covered internally
Competitive advantage over other advisors
Higher deal quality and a stronger negotiating position
Example: Contributions from ABRAMS wiki in target search:
Expand breadth via the supply‑chain view — not just the “visible” firms (large, public, registered) but also critical niche suppliers or specialized customers.
Cluster by role in the value chain — tier‑1, tier‑2, bottleneck, innovation supplier.
Quickly surface hidden champions — e.g., firms with little financial visibility that are key suppliers to industry leaders.
Regional additions — trade‑flow visibility reveals alternative targets across regions (e.g., reshoring options).
Value: the longlist becomes substantially broader and more strategic by factoring in operational relevance.